Automation specialist Hambi Maschinenbau has developed a system that automates the cutting, handling, and stacking of heavy reinforcing steel mesh – a task that previously required up to six human operators. By integrating Mitsubishi Electric’s drive and control technologies connected via CC-Link IE TSN, Hambi has achieved millimetre-level precision and seamless synchronisation across motion, safety, and vision systems in a single, unified network.
In the production of reinforcing steel mesh, long lengths of wire are welded into large mats, which must then be cut to size and stacked for transport. This was a labour-intensive process involving multiple workers to lift, align, cut, and stack the heavy meshes. It was also considered a difficult task to automate, as weight and flexibility of the mats means that even small deviations in alignment can cause major issues.
However, Van Merksteijn International B.V., a steel processor, was determined to overcome these challenges. It reached out to Hambi to develop an automated solution that could detect and compensate for any alignment variations in real time.
The result was the ASA (Automatic Cutting System) – a six-metre-high, 40-metre-long machine that automates every stage of the process, from lifting the top mat in a stack to cutting and turning sections for compact stacking.
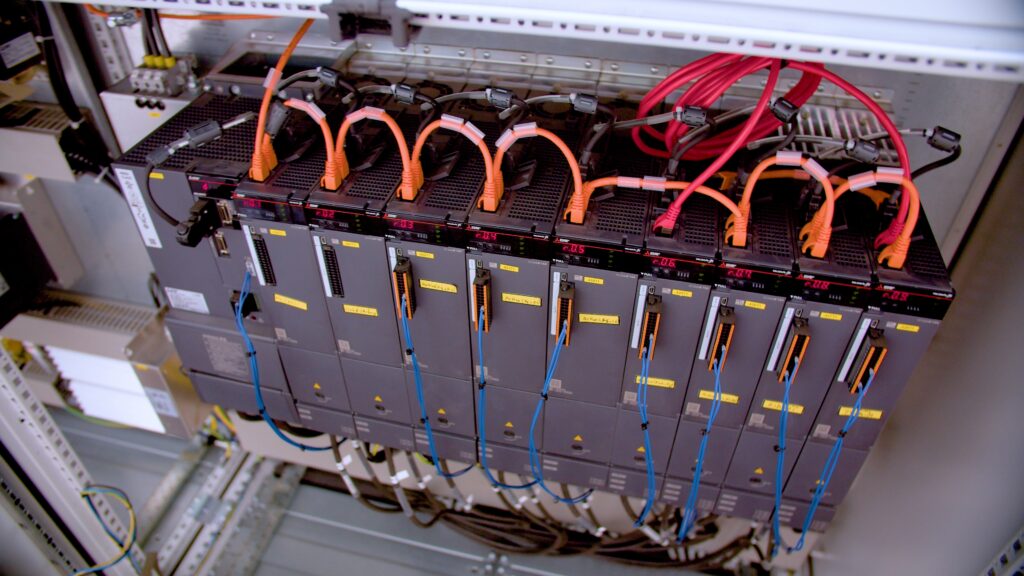

Precision through synchronisation
The system uses six grippers, each capable of independent three-axis movement. As the mesh bends under its own weight during lifting, the grippers must dynamically adjust their positions to maintain even tension and prevent deformation.
In total, 18 servo drives coordinate this movement, with additional drives handling transportation, turning, and stacking. Synchronisation between these drives, as well as with the image processing system and safety controls, is critical to ensure stability and precision.
That’s why Hambi decided to link every part of the system – including servo drives, safety PLCs, frequency inverters, and controllers – via CC-Link IE TSN. The high-speed, deterministic communication provided by the open Ethernet standard allowed the team to achieve millimetre-level precision when gripping and positioning the steel mesh, even as it naturally bends and shifts during lifting.
The technology’s gigabit bandwidth also allows all system components to share a single unified network.
“Communication via CC-Link IE TSN is particularly important,” explains Marc Orgassa, Managing Director of Orgassa GmbH, Hambi’s long-term automation partner. “It allows us to ensure that the various system components and controllers are synchronised with the drives. This is an important prerequisite, as image processing naturally requires the exact position of the grippers.”
Following two years of development, the ASA system was commissioned at Van Merksteijn’s site in spring 2024.
 Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer
Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer