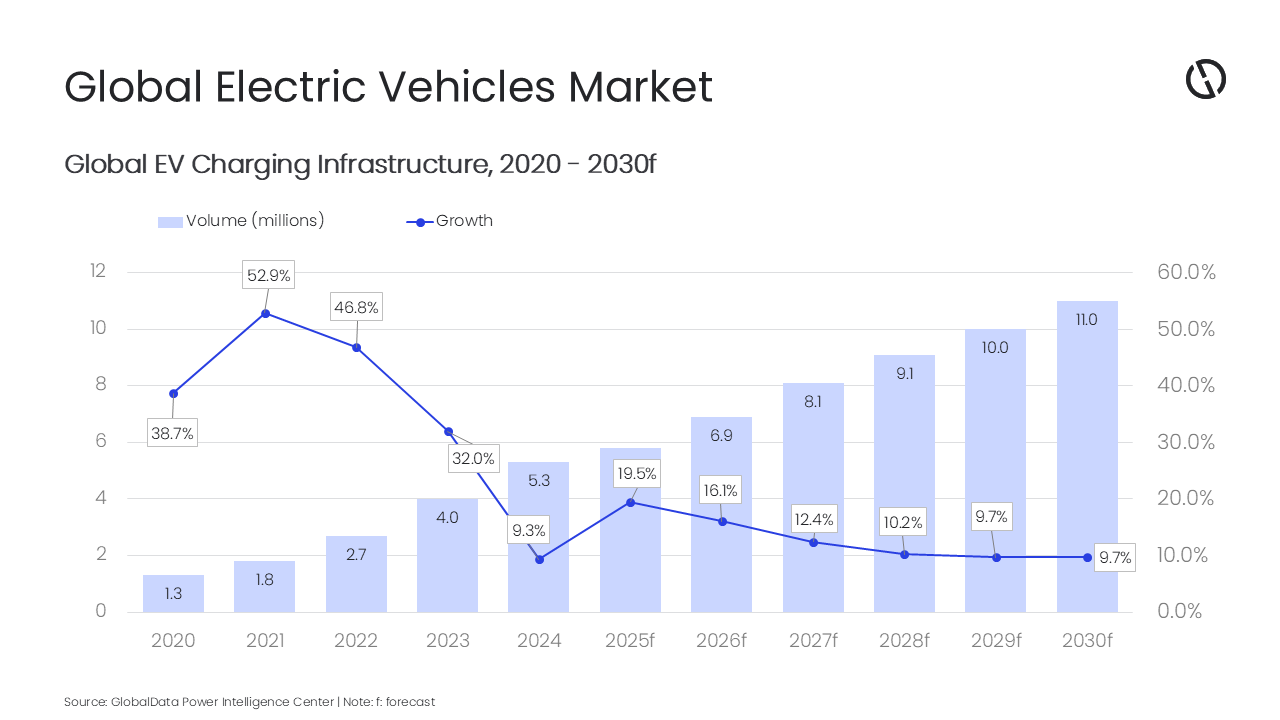
With electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerating, driven by stricter government emissions regulations worldwide, the demand for a strong EV charging network is rapidly increasing. Countries such as the US and China have seen especially fast growth in EV uptake, supported by substantial public investment in charging infrastructure. The global EV charging infrastructure market is set to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.6% from 5.8 million units in 2025 to 11.0 million units in 2030, forecasts GlobalData.
GlobalData’s latest report, Electric Vehicles in Power: Strategic Intelligence, shows that rising EV adoption is intensifying the need for more public charging stations to keep pace with growing electricity demand. Investments are being directed toward strengthening high-speed charging capabilities, highlighting the industry’s emphasis on infrastructure build-out to support the expanding EV market.
For instance, in May 2024, Charge Zone raised $19 million from British International Investment to scale up its EV charging infrastructure. Earlier, in July 2023, GLIDA announced plans to invest about $1.2 million to expand its charging-station network.
Rehaan Shiledar, Senior Power Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “Global outlook for battery electric vehicles (BEVs) remains strong, supported by increasing consumer uptake, fast-paced technology advances, and supportive government policies. BEV sales are projected to rise significantly, growing the worldwide EV fleet over the coming years in line with existing policy directions and driving higher battery demand. While China continues to lead the market, demand is spreading more broadly, with meaningful growth in both emerging economies and mature markets such as the EU and the UK.
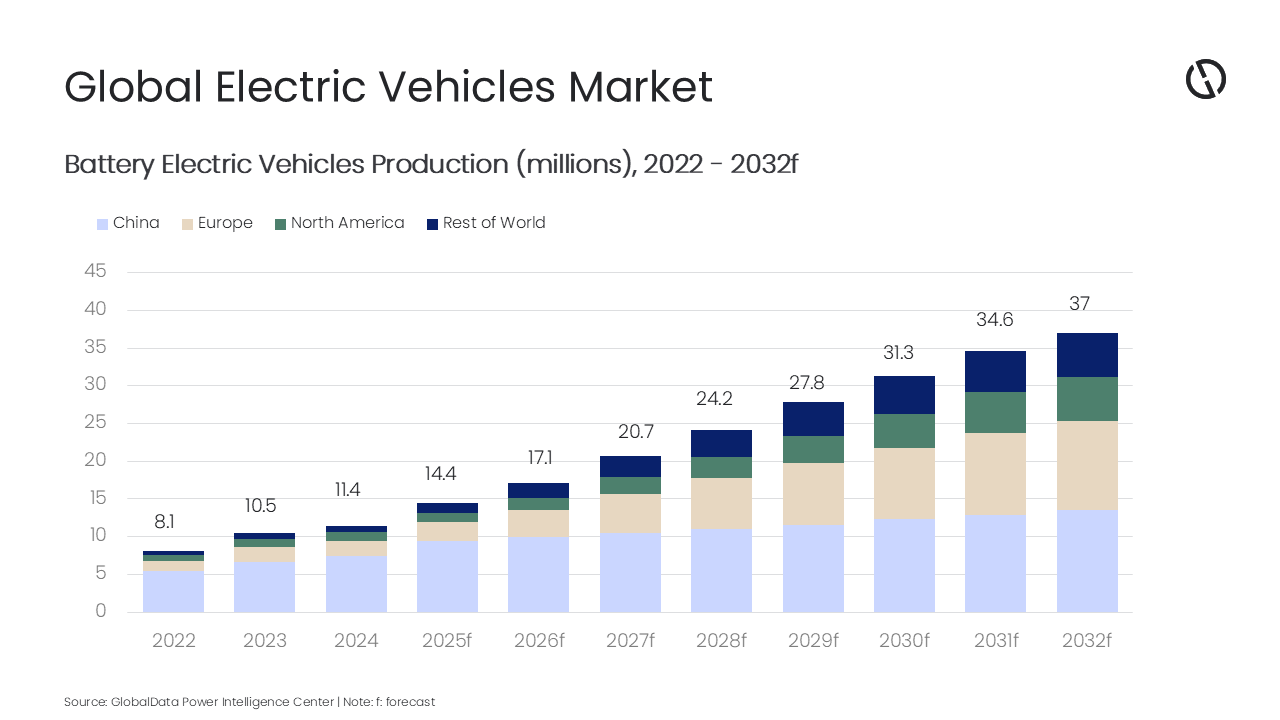
China is a leader in EV production, accounting for over half of global sales and production due to strong government support, significant investment in infrastructure, and advanced domestic manufacturers. China delivered about 7.5 million units of BEVs in 2024 and is expected to produce about 13.5 million units of BEVs by 2032.
Europe is estimated to reach 11.8 million units by 2032, whereas North America and the rest of the world are estimated to produce about 5.9 and 5.8 million units of BEVs, respectively, by 2032. The global BEV production stood at 11.4 million units in 2024 and is estimated to reach approximately 37 million units in 2032.
Shiledar continues: “Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is rapidly gaining traction driven by the increasing adoption of EVs, the need for grid stabilization with the rise of renewable energy sources, and supportive government policies. The technology enables EVs to return stored energy to the power grid from their batteries. V2G is part of the broader vehicle–grid integration paradigm and can supply electricity to homes, commercial buildings, and any loads tied to the grid. The parallel expansion of EV fleets and smart-grid capabilities has driven the development of V2G, and demand for the technology is expected to rise alongside further EV adoption and smart-grid deployment.”
Numerous companies are actively advancing V2G solutions to capitalize on this growth. Companies such as Vattenfall, E.ON, and Nuvve are developing and implementing vehicle-to-grid technology, using electric vehicles as mobile energy storage assets.
Shiledar concludes: “The EV market is expected to grow steadily in the years ahead, supported by strong government incentives, ongoing technology improvements, and rising consumer preference for cleaner transportation. The most immediate impact of a larger EV fleet is increased electricity demand, as more vehicles plug in for charging and add new load to the power system. To handle this growth, utilities will need to strengthen the grid by upgrading transformers, substations, and distribution feeders. Deploying smarter grid solutions such as smart charging and vehicle-to-grid technologies—can help align charging with grid conditions, reduce peak demand, support grid stability, and enable greater integration of renewable energy.”
 Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer
Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer