As the sophistication and severity of cyber-attacks/breaches continue to intensify, cybersecurity has now rightfully become a major issue at the forefront of the public eye.
Interested in cyber security, Reboot Online Marketing analysed the latest data from the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) to establish which type of major cyber security incidents were reported to them the most from April 2020 to March 2021 (2020/21).
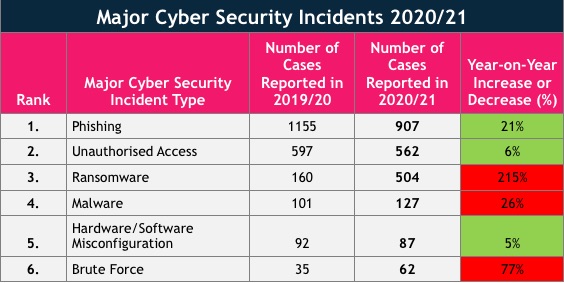
The six major ‘type’ of cybersecurity incidents included: phishing, unauthorised access, ransomware, malware, hardware/software misconfiguration and brute force.
Analysis of the results from the researchReboot Online Marketing found that the ICO received 907 reports of phishing between April 2020 to March 2021 – the equivalent of two phishing incidents a day! Compared to April 2019 to March 2020, it represents 21% drop in year-on-year phishing incidents.
In second place there were 562 cases of unauthorised access brought to light to the ICO from April 2020 to March 2021. Despite this, it was a 6% fall from April 2019 – March 2020, where there were 597 incidences of unauthorised access.
Ransomware was the cybersecurity incident which experienced the biggest year-on-year increase at 215%. In 2020/21 there were a total of 504 cases reported to the ICO in contrast to the 160 the year before (2019/20).
Malware (127) and hardware/software misconfiguration (87) are among the other major cyber security incident types that were made aware to the ICO over 80 individual times each during 2020/21, respectively ranking fourth and fifth.
At the other end in sixth place is brute force, as the ICO were alerted of 62 occurrences of the cryptography-centric attack in 2020/21. Alarmingly, it symbolises a 77% increase in brute force attacks when shadowed against 2019/20, when 35 incidents were recorded by the ICO.
Overall, when combining the figures together for the six categories, there were a grand total of 2,249 major cybersecurity incidents reported to the ICO in 2020/21.
Major cybersecurity incident types explained
What is phishing? Phishing is a cybercrime where deceptive emails and/or websites are used by opportunistic cyber criminals to trick targets into handing over their personal data/information such as banking details.
What is unauthorised access? Unauthorised access is when a cybercriminal gains unauthorised access to a computer network, server, program, website, or system using someone else’s account/login credentials.
What is malware? Malware is any software designed by a cybercriminal to intentionally cause damage to a computer network, server, program, website, or system. The malicious software can perform a wide variety of functions such as stealing, encrypting, or deleting sensitive data as well as monitoring a target’s computer activity.
What is ransomware? A form of malware, a ransomware attack by a cybercriminal encrypts a victim’s files. To restore access to the data, the victim must meet the payment demands of the cybercriminal, hence being held to ransom.
What is hardware/software misconfiguration? Hardware/software misconfiguration is a failure to adequately implement all the security controls of a piece of hardware or software. Alternatively, implementing the security controls, but doing so with errors. In either scenario, potentially leaving sensitive data at the risk of being exploited by cybercriminals.
What is brute force?
A brute force attack is when a cybercriminal uses a trial-and-error process to guess login information. An attacker tries as many passwords or passphrases as possible in the hope they will eventually identify the correct one.
Methodology for the research
- Reboot Online Marketing analysed data from the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) to identify how many times six different major cybersecurity incidents had been reported to the ICO from April 2020 to March 2021 (2020/21).
- To achieve this, Reboot Online Marketing established phishing, unauthorised access, ransomware, malware, hardware/software misconfiguration and brute force as the six major cybersecurity incident types.
- Reboot Online Marketing then calculated how many cases for each of the six major cyber incident types were reported to the ICO in four different quarters (Q1 – Apr to Jun 2020, Q2 – Jul to Sep 2020, Q3 – Oct to Dec 2020, Q4 – Jan to Mar 2021).
- Once the figures for each of the six major cybersecurity incident types were established for each of the four quarters, the individual figures for the four quarters were added together to establish a collective total figure for a 12-month period.
- The figures were then ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of cases reported to the ICO for each major cybersecurity incident type.
- Stage three was repeated but this time in the context of 2019/20 data (Q1 – Apr to Jun 2019, Q2 – Jul to Sep 2019, Q3 – Oct to Dec 2019, Q4 – Jan to Mar 2020).
- The 2020/21 case figures for each of the six major cybersecurity incident types were compared against the 2019/20 case figures to see if there was a year-on-year increase or decrease (represented as percentages) in case numbers for each of them.
- The ICO is a non-departmental public body that reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom (UK) and was set up “to uphold information rights in the public interest, promoting openness by public bodies and data privacy for individuals”.
 Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer
Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer