At least 6.6m tonnes/year, or 26%, of Europe’s ethylene production capacity is threatened by oil refineries running at reduced rates or ceasing production, according to new analysis by ICIS, an independent commodity intelligence service for the global energy, petrochemical and fertiliser industries.
The ethylene is produced by crackers attached to refineries hit by collapsing demand for petroleum products, including jet fuel, as coronavirus-linked restrictions cut road and air transport; aviation has come to a standstill across the region.
These ethylene crackers may be forced to reduce operating rates or close because they rely mainly on naphtha or liquified petroleum gas (LPG) feedstocks sourced from the refineries to which they are linked.
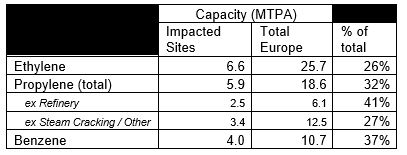
ICIS analysis suggests the 6.6m tonnes/year represent about 50% the refinery-linked steam cracking capacity in Europe, and 26% of the region’s steam cracking capacity.
For propylene, 5.9m tonnes/year of capacity is linked, while for benzene the figure is 4.0m tonnes/year.
The analysts are aware of around 6.5m bbl/day of oil refining capacity that is not operating at typical capacity.
There are some planned stoppages, but most are due to reduced fuels demand from coronavirus and associated lockdowns. The experts believe that at least 2.2m bbl/day of reductions are in place, versus the expected forecast throughput of 12.2m bbl/day for Europe.
“The reduction is almost certainly even higher in reality and could be as high as 5m bbl/day when considering those sites which do not share such information,” according to Michael Connolly, Senior Consultant at ICIS global refining team.
The refineries are operating in the range of 50-60% utilisation, which reflects the typical minimum turndown for most distillation units.
However, the crackers that are directly linked are probably able to run at higher utilisation rates than this.
Connolly said that while the normal feedstock of light naphtha is reduced in tandem to refinery utilisation, the mid-portion of naphtha that is generally used in the gasoline pool (via further processing) can be directed to steam cracking instead, which produces a lower quality feed than light naphtha.
“This would assist in decoupling refinery-cracker utilisation rates, to enable the better margins on naphtha cracking to be captured and meet supply demand for the types of polymers that are essential for the fight against coronavirus,” added Connolly.
This ability could be maintained while the upstream refinery is operating. But if the refinery is forced to shut down completely, many of these crackers are unlikely to have the logistics to support importing sufficient feedstock to maintain operations, particularly inland crackers which represent 2m tonnes/year of this ethylene capacity.
 Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer
Engineer News Network The ultimate online news and information resource for today’s engineer